ultrasonic scanning methods
Based on the position of the transducer and the output displayed in the CRO screen, we can classify the scanning methods into three types viz.,
(i) A- Scan
(ii) B - Scan
(iii) T - M- Scan (or) C-Scan
(i) A- Scan
(ii) B - Scan
(iii) T - M- Scan (or) C-Scan
i) A-Scan (or) Amplitude mode display
Amplitude mode display gives only the one dimensional information about the specimen. In this, a single transducer is used to transmit and receive the pulses from the specimen.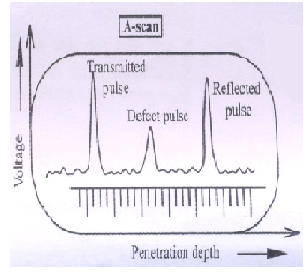

The received (or) reflected echo signals from the specimen is given to Y -plate and time base is connected to X- plate of CRO, so that they are displayed as vertical spikes along horizontal base line as shown in above fig.The height of the vertical spikes corresponds to the strength of the echo from the specimen. The position of the vertical spike from the left to right along the X-axis corresponds to the depth of penetration i.e., it gives the total time taken by the ultrasonic sound to travel from transmitter to the specimen and from the specimen to the receiver.
Thus by passing the ultrasonic waves of known velocity and by noting the time delay, we can find the distance at which the defect or flaws are present.
ii) B-Scan (or) Brightness mode display

B-Scan (or) Brightness mode display gives a two-dimensional image. In B-scan the transducer can be moved rather than keeping in a fixed position. As a result each echo is displayed as dot on the screen as shown in above fig. The brightness and size of the dot depends on the intensity and strength of the reflected echo pulses respectively. The distance between the two dots gives the penetration depth. Thus, B-scan provides exact information about the internal structures of the specimen.